Costochondritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Costochondritis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone (sternum). This inflammation can lead to sharp or aching chest pain, especially during deep breathing, sudden movements, or upper body activity. Although costochondritis is not life-threatening and often improves over time, it can significantly affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
What Causes Costochondritis?
The exact cause of costochondritis is still unclear. However, several factors are known to increase the risk of developing this condition:
1. Physical Strain
Repetitive movements, frequent bending, heavy lifting, or poor posture can place excessive stress on the rib joints, leading to irritation and inflammation.
2. Trauma or Chest Injury
Direct impact, accidents, or sudden force to the chest area may trigger inflammation of the costochondral joints.
3. Respiratory Infections
Persistent coughing or frequent sneezing from respiratory infections can strain the rib cage and contribute to chest wall inflammation.
4. Musculoskeletal Conditions
Underlying conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or fibromyalgia may increase susceptibility to costochondritis.
Common Symptoms of Costochondritis
Symptoms can vary from person to person, but the most frequently reported signs include:
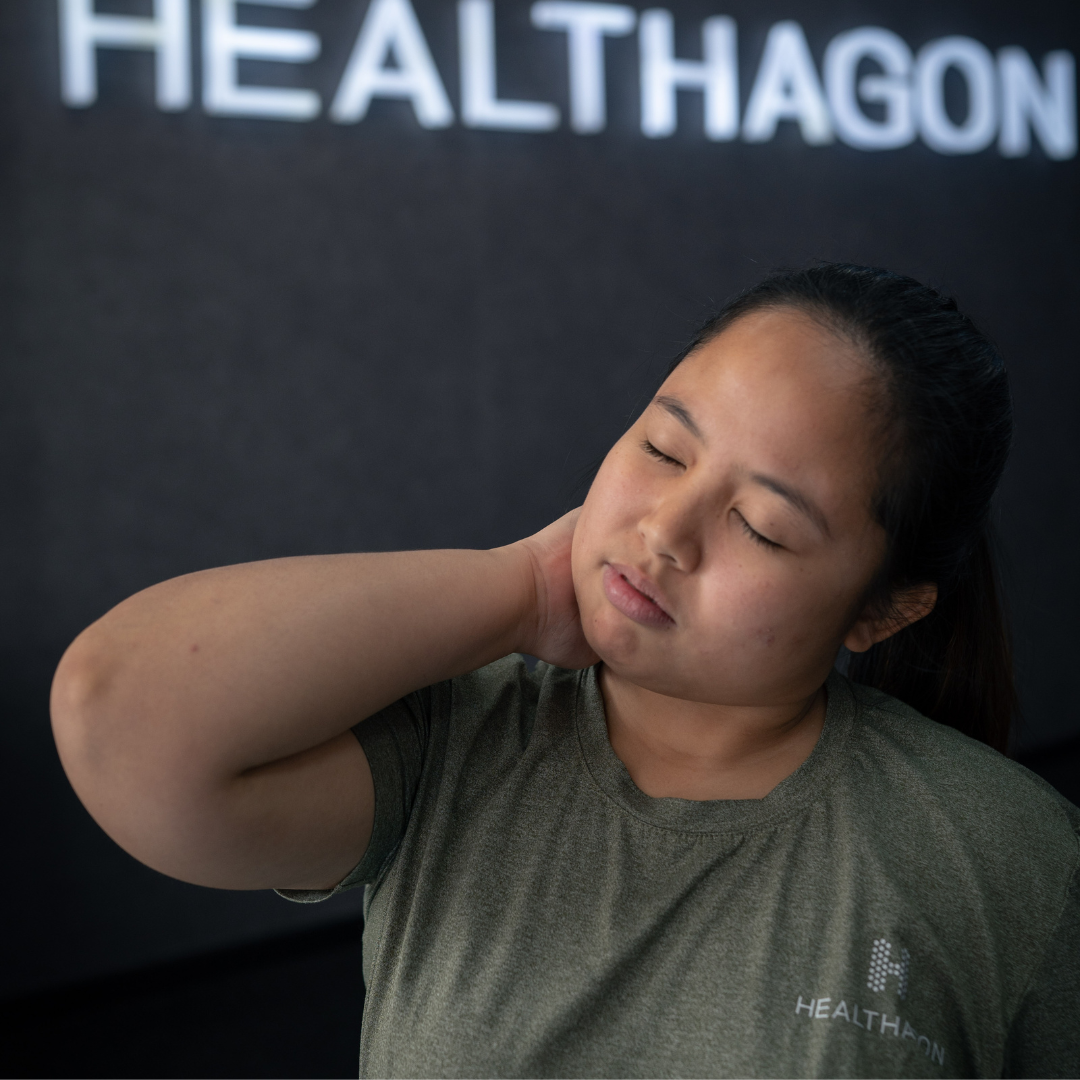
• Chest Pain
Sharp, stabbing, or aching pain felt on one or both sides of the chest, often near the breastbone.
• Localized Tenderness
Pain that worsens when pressing on the affected rib joints.
• Pain with Movement or Breathing
Discomfort that increases with coughing, sneezing, deep breathing, sudden upper-body movements, or lying down.
How Is Costochondritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing costochondritis can be challenging because its symptoms may resemble other conditions such as heart problems, chest infections, arthritis, fibromyalgia, or Tietze syndrome.
A healthcare professional may:
- Review your medical history
- Perform a physical examination of the chest and surrounding muscles
- Recommend imaging tests such as X-ray or MRI to rule out other conditions
Treatment Options for Costochondritis
Treatment mainly focuses on reducing inflammation and relieving pain. Common management approaches include:
1. Pain Relief Medication
Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help reduce pain and swelling. In persistent or severe cases, steroid injections may be recommended.
2. Rest and Heat or Cold Therapy
Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms is essential. Applying heat or cold packs can help manage pain and inflammation at home.
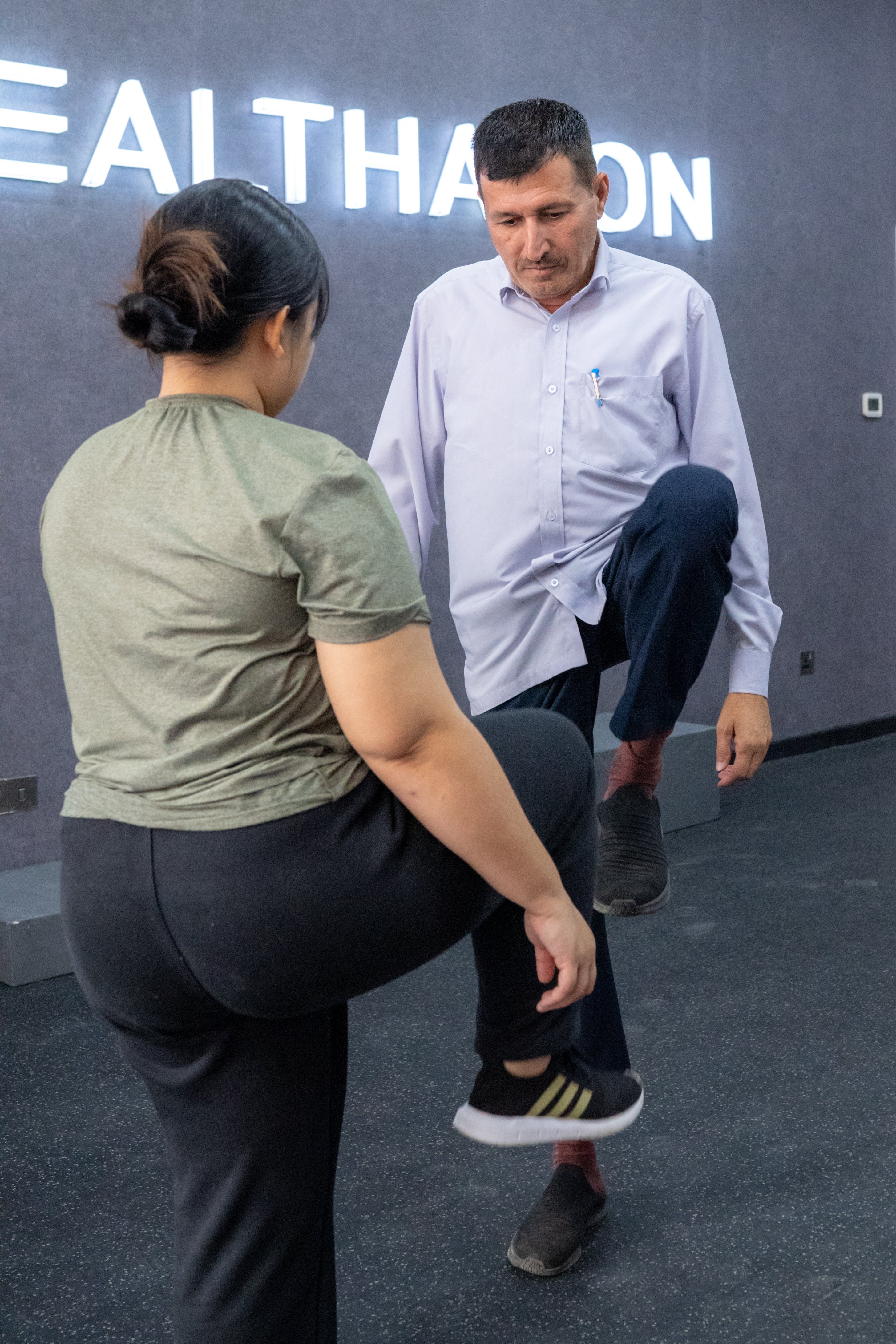
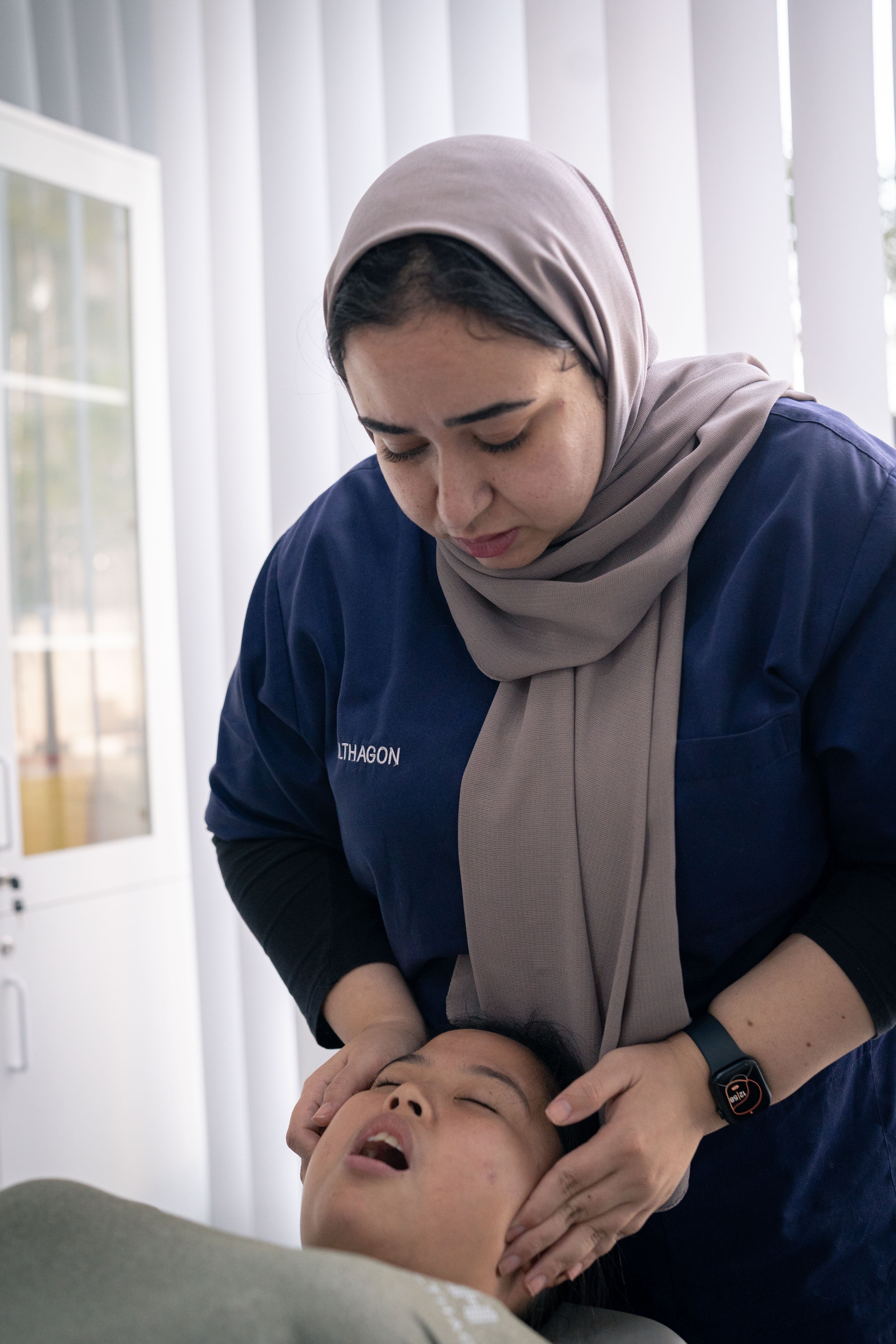
3. Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy plays a key role in recovery and may include:
- Manual therapy
- Gentle stretching
- Therapeutic exercises to improve mobility, posture, and chest stability
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintain proper posture
- Avoid heavy lifting and repetitive strain
- Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
- Stay active with guided, low-impact movements

Conclusion
Costochondritis can be uncomfortable and sometimes limiting, but with proper understanding, early diagnosis, and the right treatment approach, symptoms can be effectively managed. Physiotherapy and lifestyle changes play an important role in reducing pain and preventing recurrence.
If you are experiencing persistent or severe chest pain, it is important to seek professional medical advice to rule out other serious conditions and receive appropriate care.